Lower back pain is very common. From time to time it occurs in 90% of the population, and it is not always possible to identify the true causes. More often, lumbar pain occurs after intense physical activity and may indicate back problems or diseases of the internal organs. The diagnosis determines what treatment will be - conservative or surgical.
Causes and nature of pain
Lower back pain can be acute, sudden, occur after physical effort and lead to a forced body position. Pain in the lower spine is constant, aching or pulling, accompanied by stiffness, numbness, and tingling.
The intensity of pain in the lumbar region also varies: from mild, which does not interfere with everyday life, to unbearable, which forces you to take painkillers and lie in bed. Sometimes the pain spreads beyond the back, affecting the buttocks, thighs and even legs.
The pain may go away on its own, but in the worst case it worsens, causes discomfort and leads to limited mobility. In order not to live with pain, you need to find out the reason why your lower back hurts. Most often, a preliminary diagnosis can be made based on the nature of the pain.
Shingles
Such lower back pain is not limited to the lumbar region. They spread throughout the back, along the torso, and can radiate to the lower abdomen, gluteal region and legs.
The most common cause of lumbar pain in the lower back is osteochondrosis. This is a chronic disease of the spine that leads to pinched nerve endings and pain. Symptoms are complemented by sensory disturbances, numbness, and disorders of the internal organs.
The source of the girdle pain may be located above the lumbar level and not be associated with diseases of the spinal column. In this case, the patient simply feels pain in the lower back, but the pain itself is localized in the chest area.
The cause of shingles pain in the lower back can be diseases of the internal organs, especially the heart, lungs, and gastrointestinal tract. For example, pancreatitis, cholecystitis, stomach or duodenal ulcer, pleurisy, pneumonia, heart attack.
The pain is caused by irritation of the nerve fibers of the organs.
Soreness below the lumbar level in the coccygeal region is a sign of diseases of the kidneys and reproductive organs.
When walking
The lumbar region is represented by 5 vertebrae, intervertebral discs and ligaments. Many nerve endings that are involved during walking depart from it. With any lower back disease, nerves may become pinched during movement, which leads to lower back pain.
The intensity and nature of pain depends on the scale of the lesion. If it hurts to move, then this is a sign of osteochondrosis or herniated intervertebral discs. In the latter case, terrible pain occurs in the lower back while walking. It subsides a little when a person is in a sitting position.
The cause of lower back pain when walking can be excessive physical activity the day before. It appears only at the moment of movement and disappears at rest, there are no accompanying manifestations.
Acute pain
Acute pain in the lower back is also called lumbago or lumbago. It immobilizes and forces you to take a forced position. An attack of terrible lower back pain can last only a few minutes, and sometimes lasts for several days.
One of the common causes of back pain in the lumbar region is excessive physical activity, which leads to sprains, strains or muscle spasms. This can happen due to sudden movement, heavy lifting, poor body rotation, or awkward posture. Muscle inflammation is provoked by hypothermia or being in a draft.
If you sprain or strain when moving, the lower back hurts even more.
The cause of severe lower back pain can be lumbosacral radiculitis or a herniated disc. In this case, when you stand up, bend over, or walk, your lower back hurts even more.
The cause of acute lumbar pain can be other diseases of the musculoskeletal system:
- osteochondrosis;
- arthrosis of the facet joints;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- osteoporosis;
- spondylosis;
- spondylolisthesis;
- spinal injuries;
- protrusion;
- infectious diseases of the spinal column (tuberculosis, epidural abscess, osteomyelitis);
- spinal canal stenosis;
- rachiocampsis;
- tumors;
- Bekhterev's disease.
The reason why the lower back and tailbone hurt can be diseases of the internal organs. Acute pain syndrome occurs with cholecystitis, pancreatitis, inflammatory diseases of the reproductive system, pyelonephritis, renal colic, and abdominal artery aneurysm.
Constant pain
Constant pain in the lower back is often aching in nature. The intensity of pain may increase with hypothermia, physical activity, injury, or unsuccessful movements. A common accompanying symptom of regular lower back pain is stiffness of movement. It especially manifests itself after rest.
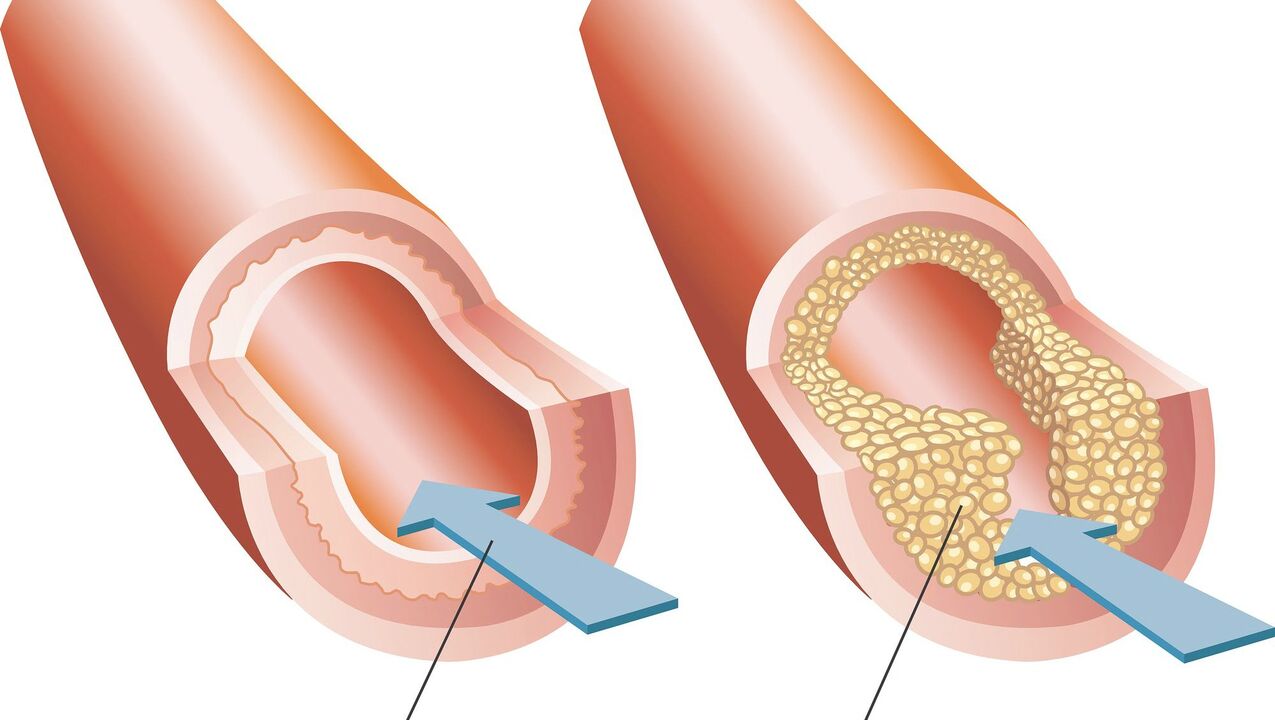
The cause of constant pain in the lumbar region is vascular pathologies, which lead to poor circulation. For example, vascular atherosclerosis, phlebothrombosis, thrombophlebitis.
The lower back can also hurt due to inflammatory and degenerative processes of the musculoskeletal system.
It's a dull pain
Aching pain in the lower back often indicates diseases of the internal organs. If your back hurts in the back, this may be a symptom of the following diseases:
- pyelonephritis;
- kidney stone disease;
- endometriosis;
- inflammation of the uterus or appendages;
- ectopic pregnancy.
The peculiarity of all these diseases is that lower back pain occurs against the background of a general deterioration in well-being.
If the spine hurts in the middle, then this indicates pancreatitis or cholecystitis.
When you're sitting
If the lower back hurts while sitting, this indicates excessive physical activity or serious pathologies of the spine. In this case, the pain in the lower back is sharp or burning. Aching dull pain, on the contrary, can be caused by a sedentary lifestyle.
The reason why the lower back hurts after sitting is pinched intervertebral discs.
If the cause is radiculitis, hernia, tumor, protrusion, then when standing up the lower back hurts even more.
Pain can occur with diseases of the pelvic organs and kidneys.
When you're standing
If your lower back hurts very much when standing, it could be radiculitis. To reduce pain, you should change your position. The lumbar spine may hurt in an upright position due to a hernia.
Which doctor treats low back pain?
If your lower back hurts, you should contact the following specialists for treatment:
- orthopedist;
- neurologist;
- vertebrologist
An osteopath, reflexology or chiropractor may take part in the therapy. Sometimes the help of a surgeon, gastroenterologist, gynecologist, urologist, nephrologist and oncologist is required.
Going to the hospital should be mandatory in the following cases:
- pain caused by injury;
- pain extends beyond the back, accompanied by other symptoms (numbness, urinary or fecal incontinence);
- lasts more than 3 days or appears again after some time.
Diagnostics
To understand why there may be pain in the lumbar region, the doctor conducts a visual examination and listens to the patient’s complaints. Based on what he saw and heard, he draws up a clinical picture and can make a diagnosis or prescribe additional examination.
During the examination, it is important to determine the cause-and-effect relationship.
Diagnosis of pain in the lumbar region may include the following examination methods:
- blood and urine tests;
- X-ray of the spine;
- CT or MRI;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs;
- chest x-ray;
- ECG;
- fibrogastroduodenoscopy.
Treatment
If lower back pain occurs, treatment directly depends on what caused it. Immediately after the onset of a painful attack, it is worth limiting physical activity for 2-3 days, but bed rest is also not recommended. It is better to sleep in the fetal position with a pillow between your knees. This way the back is unloaded.
In case of severe pain, you can take a pain reliever. If pain occurs as a result of an injury, you should apply cold to the sore spot.
For spinal canal stenosis, injection blockade with steroid drugs and analgesics is used.
Do not forget that long-term use of painkillers is not an option. Tablets only mask the problem, and do not get rid of it.
Pain is most often treated with medications (NSAIDs, chondroprotectors, muscle relaxants, vitamin complexes), massage, manual therapy, exercise therapy (Bubnovsky complex) and physiotherapeutic procedures. Acupuncture is becoming increasingly popular to relieve muscle tension.
Most often, pain can be relieved within 4-6 weeks.

If conservative therapy is ineffective (mainly in the case of a hernia), surgical intervention is performed. During the operation, the hernia is removed. The patient immediately feels significant relief.
What can't you do?
You should not self-medicate or use painkillers or anti-inflammatory drugs for a long time. If the pain does not subside within 3 days, you should visit a doctor.
You cannot perform a set of exercises on your own. To prevent the pain from getting worse, the training program should be prescribed by a specialist. In case of exacerbation of diseases of the spinal column, massage and physical exercise are generally contraindicated until relief occurs.
In case of injury, you cannot adjust the vertebrae yourself or warm up the affected area.
Prevention
Preventive measures:
- do not lift weights;
- do not make sudden movements, avoid excessive physical exertion;
- sleep on a hard mattress;
- observe a rest regime;
- lead an active lifestyle, walk at least 1 hour a day;
- for sedentary work, do it every 40-50 minutes. warm-up break;
- do exercises every day, hanging on the horizontal bar is useful;
- do not overcool;
- Healthy food;
- take vitamin complexes containing calcium.
To prevent lower back pain, you should not overload your back. We must not forget that the functioning of internal organs depends on the health of the spine.
If your back hurts, you shouldn’t hesitate; you need to seek help from a doctor. They will determine the true cause and help avoid serious health problems.



















